
 |
| Head-Mounted Display Devices |
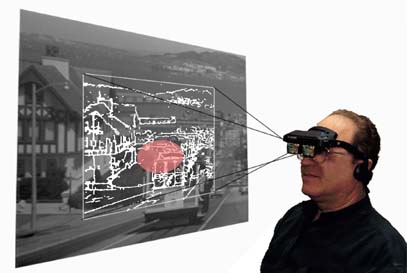 As
part of the effort to adapt image enhancement technologies to the visually
impaired, we are working on the development of augmented vision systems for use
by visually impaired. A newly developed image enhancement technique enables the
projection of enhancement outline on the natural view of the environment using
see-through, head-mounted display (HMD). An open peripheral design for such a
system permits the use of the full peripheral field while the enhancement is
limited to the central HMD field. This HMD approach is a significant advance in
low vision aids. Studies on the visual effects of HMD in low vision and in
normally sighted observers are part of this program. In this direction we are
developing (with NASA support) a new stereo display system that is free from the
problem of conflict between accommodation and convergence. We are also working
with many of the HMD manufacturers on testing comfort and safety of their new
devices.
As
part of the effort to adapt image enhancement technologies to the visually
impaired, we are working on the development of augmented vision systems for use
by visually impaired. A newly developed image enhancement technique enables the
projection of enhancement outline on the natural view of the environment using
see-through, head-mounted display (HMD). An open peripheral design for such a
system permits the use of the full peripheral field while the enhancement is
limited to the central HMD field. This HMD approach is a significant advance in
low vision aids. Studies on the visual effects of HMD in low vision and in
normally sighted observers are part of this program. In this direction we are
developing (with NASA support) a new stereo display system that is free from the
problem of conflict between accommodation and convergence. We are also working
with many of the HMD manufacturers on testing comfort and safety of their new
devices.
Noa Rensing, Ph.D.
Cheng Qiu, Ph.D.
Navid Mostofi, Ph.D.
Shrinivas Pundlik, Ph.D.
Matteo Tomasi, Ph.D.
Zhengzhou Li, Ph.D.
Fernando Vargas-Martin, Ph.D.
DoD Grant W81XWH-16-1-0033, "Active Confocal Imaging System for Visual Prostheses"
NIH Grant R01EY12980-09S1, "Revision Competitive ARRA Supplement to Engineering Approach to Low Vision Rehabilitation"
NIH, EY05957, "Model-based Image Enhancement for the Visually Impaired"
NIH Grant RO1EY12890, "Engineering Approaches to Low Vision Rehabilitation"
NIH EY12912 (SBIRII) Video display for the visually impaired (awarded to the MicroOptical Corp)
NIH Grant 1R24EY12890, "Engineering Approaches to Low Vision Rehabilitation"
NASA-Ames Cooperative agreement No. NCC 2-1039, PI. "Development and Evaluation of a Binocular Stereoscopic Display System with Coupled Convergence and Accommodation Demands"
DOE/ DE-FG 02-91ER61229 (Robert Webb, PI). Center of Excellence of Lasers in Medicine
Peli E. (2007) Wide-band image enhancement. US patent No. 7,280,704 (continuation of US patent 6,611,618). [PDF 2.0 MB]
Peli E, Gupta A. (2016) Providing focus assistance to users of a head mounted display. US Patent US9523853B1 [ PDF 0.8 MB ]
Spitzer M, Gallant B, Peli E. (2019) Display of binocular overlapping images in a head mounted display. US Patent US10261319B2 (Assigned to Google, Inc.) [ PDF 2MB]
Hwang AD and Peli E. (2020) Methods and systems for adjusting contrast in devices US Patent 10755673B2 (assigned to Schepens Eye Research Institute) [ PDF 2.5 MB ]
Peli E. (2020) Reducing visually induced motion sickness in head mounted display systems US Patent 10628994B2 (Assigned to Google, Inc.) [ PDF 1,8 MB ]
Behnam Bastani and Eliezer Peli. (2020) Virtual reality system using super-resolution US Patent 10572761B1 (Assigned to Google, Inc.) [ PDF 1,7 MB ]
Pundlik S, Yi H, 2, Liu R, 3, Peli E, and Luo G. (2017) Magnifying Smartphone Screen using Google Glass for Low-Vision Users. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems & Rehabilitation Engineering, 2017; 25(1): 52-61. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2546062 [PDF 1.99MB]
Hwang AD, Peli E. (2016) A New Contrast Metric for Realistic Display-Performance. In: 2016 SID International Symposium. Digest of Technical Papers, 2016, 72-4; 983-986. [ PDF 1.83MB]
Hwang AD, Peli E. (2014) An Augmented-Reality Edge Enhancement Application for Google Glass. Optometry and Vision Science, 91(8), 1021-1030. [PDF 1.53MB]
Hwang AD, Peli E (2014) Augmented Edge Enhancement for Vision Impairment using Google Glass. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 45: 305?307. doi: 10.1002/j.2168-0159.2014.tb00082.x [ PDF 666KB]
Hwang AD, Peli E. (2014) Augmented Edge Enhancement on Google Glass for Vision-Impaired Users. Information Display, SID, 32(3), 16-19 [PDF 11.1MB]
Luo G, Peli E. (2011) Development and evaluation of vision rehabilitation devices. 33rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC '11), Boston, Massachusetts USA, August 30 - September 3, 2011. pp 5228-5231. [PDF 1.05 MB ]
Li Z, Luo G, Peli E. (2011) Image Enhancement of high digital magnification for patients with central field loss. In: SPIE-IS&T Electronic Imaging, SPIE Vol. 7865 "Human Vision and Electronic Imaging XVI" ed. Bernice E. Rogowitz & Thrasyvoulos N. Pappas. 786516, 2011, doi10.1117/12.872531. [PDF 5.19 MB]
Apfelbaum HL, Gambacorta C, Woods RL, Peli E (2010) Inattentional blindness with same scene at different scales. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 2010 30: 124-131 [PDF 544 KB]
This is an electronic version of an article published in Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics: complete citation information for the final version of the paper, as published in the print edition of Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, is available on the Blackwell Synergy online delivery service, accessible via the journal's website at http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/OPO or http://www.blackwell-synergy.com.Luo G, Woods RL, Peli E. (2009) Collision judgment when using an augmented-vision head-mounted display device. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 50(9): 4509-4515 [PDF 547 KB]
Peli E, Luo G, Bowers A, Rensing N. (2009) Development and evaluation of vision multiplexing devices for vision impairment. International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools 18(3): 365-378 [PDF 841 KB]
Apfelbaum HL, Apfelbaum DH, Woods RL, Peli E. (2008) Inattentional blindness and augmented-vision displays: Effects of cartoon-like filtering and attended scene. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 28(3): 204-217 [PDF 1.57 MB]
This is an electronic version of an article published in Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics: complete citation information for the final version of the paper, as published in the print edition of Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, is available on the Blackwell Synergy online delivery service, accessible via the journal's website at http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/OPO or http://www.blackwell-synergy.com.Peli E, Luo G, Bowers A, Rensing N. (2007) Applications of augmented-vision head-mounted systems in vision rehabilitation. J. SID 15(12): 1037-1045[PDF 2.52 MB]
Luo G, Lichtenstein L, Peli E. (2007) Collision judgement when viewing minified images through a HMD visual field expander. Proceedings of SPIE, Ophthalmic Technologies XVII, vol. 6426, 64261Z, 2007. [PDF 6.4 MB]
Vargas-Mart?n F, Peli E. (2006) Eye Movements of patients with tunnel vision while walking. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. 47(12): 5295-5302. [PDF 956 KB]
Luo G, Peli E. (2006) Use of an augmented-vision device for visual search in patients with tunnel vision. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. 47(9): 4152-4159. [PDF 323 KB]
Zebehazy K, Zimmerman G, Bowers A, Luo G, Peli E. (2005) Establishing the Reliability of Mobility Measures to Assess the Effectiveness of Night Vision Devices: Results of a Pilot Study. Journal of Visual Impairment and Blindness. 99(10) 663-670
The American Foundation for the Blind (AFB) demanded that we do not post the preprint until it is published. After publication the paper might be found here (if AFB permits) otherwise it can be found on the
http://www.pubmedcentral.gov
through the NIH public access to archive publications.
Apfelbaum HL, Apfelbaum DH, Woods RL, Peli E. (2005) The effect of edge filtering on vision multiplexing. SID 05 Digest of Technical Papers, 2005. 1398-1401. [PDF 1.9 MB]
Luo G, Rensing N, Weststrate E, Peli E. (2005) Registration of an on-axis see-through headmounted display and camera system. Optical Engineering 44(2), 024002.
[PDF 463 KB]
© 2005 SPIE. This paper was published in Optical Engineering
and is made available as an electronic reprint (preprint) with permission
of SPIE. One print or electronic copy may be made for personal use only.
Systematic or multiple reproduction, distribution to multiple locations
via electronic or other means, duplication of any material in this paper
for a fee or for commercial purposes, or modification of the content of
the paper are prohibited.
Bowers AR, Luo G, Rensing NM, Peli E. (2004) Evaluation of a prototype minified augmented-view device for patients with impaired night vision. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, 24: 296-312. [PDF 500 KB]
This is an electronic version of an article published in Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics: complete citation information for the final version of the paper, as published in the print edition of Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, is available on the Blackwell Synergy online delivery service, accessible via the journal's website at http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/OPO or http://www.blackwell-synergy.com.Luo G, Peli E. (2004) Kinematics of visual search by tunnel vision patients with augmented vision see-through HMD. SID 2004, Digest of Technical Papers, Society for Information Display 2004. 1578-1581. [PDF 440 KB]
Barabas J, Goldstein RB, Apfelbaum H, Woods, RL, Giorgi, RG, Peli E. (2004) Tracking the line of primary gaze in a walking simulator: modeling and calibration. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers 2004. 36(4): 757-770 [PDF 4.2 MB]
Woods RL, Fetchenheuer I, Vargas-Martin F, Peli E. (2003) The impact of non-immersive HMDs on the visual field. J Soc Information Display 11(1): 191-198. [PDF 1.1 MB]
Garcia-Perez MA, Peli E. (2003) Simple non-invasive measurement of rapid eye vibration. J Sound and Vibration, 262: 877-888. [PDF 336 KB]
Wong BPH, Woods RL, Peli E. (2002) Stereoacuity at distance and near. Optom Vision Sci 79(12): 771-778. [PDF 420 KB]
Vargas-Martin F, Peli E. (2002) Augmented view for restricted visual field: multiple device implementations. Optometry and Vision Science, 79(11), 715-723. [PDF 1.0 MB]
Vargas-Martin F, Peli E. (2001) Augmented view for tunnel vision: device
testing by patients in real environments. 2001 SID International
Symposium, Digest of Technical Papers, San Jose, CA. Society for Information
Display. P-16, 602-605. [PDF
318 KB]
Peli E. (2000). Augmented vision for central scotoma and peripheral field
loss. Vision Rehabilitation: Assessment, Intervention and Outcomes.
Selected papers from Vision '99: International Conference on Low Vision. C.
Stuen et al editors, Swets & Zeitlinger, Lisse, p. 70-74. [Video
Simulations] [PDF
(228 KB)] or [html]
Peli E. (1999) Simple 1-D image enhancement for head-mounted low vision aid. Visual Impairment Research 1(1):3-10. [PDF 183 KB]
Peli E. (1999) Optometric and perceptual issues with head-mounted display (HMD). In: Mouroulis P, ed. Optical Design for Visual Instrumentation. McGraw-Hill, New York. pp. 205-276. [PDF 2.48 MB]
Peli E. (1998) The visual effects of head-mounted display (HMD) are not distinguishable from those of desk-top computer display. Vision Res 38: 2053-2066. [PDF 203 KB]
Fischer RE, Reiley DJ, Pope C, and Peli E. (1997). The Capability of Virtual Reality to Meet Military Requirements. Paper presented at the RTO HFM Workshop held in Orlando, USA, 5-9 December 1997, and published in RTO MP-54.[PDF 726KB]
Peli E. (1996) Visual and optometric issues with head-mounted displays. In: Proceedings of the IS&T Optics & Imaging in the Information Age 1996, The Society for Imaging Science and Technology 364-369. [PDF 328 KB]
Peli E. (1995) Real vision & virtual reality. Optics & Photonics News 6(7): 28-34. [PDF 1.43 MB]
Peli E. (1994) Head-Mounted Display as a Low Vision Aid. 1994 Virtual Reality Conference Proceedings, California State University Northridge. [HTML 38 KB]
Peli E. (1990) Visual issues in the use of a head-mounted monocular display. Optical Engineering 29(8): 883-892. [PDF 502 KB] © 1990 SPIE. This paper was published in Optical Engineering and is made available as an electronic reprint (preprint) with permission of SPIE. One print or electronic copy may be made for personal use only. Systematic or multiple reproduction, distribution to multiple locations via electronic or other means, duplication of any material in this paper for a fee or for commercial purposes, or modification of the content of the paper are prohibited.